fit for duty testing
accurately testing equipment for safety
Respiratory Mask Fit Test
TruTest Labs understands how to conduct a test, recognize invalid tests, and properly clean and maintain equipment for a respirator mask.
Did you know that fit testing for a respirator mask is required by the U.S. Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) and is crucial to respiratory safety?
Tight-fitting respirators must seal to the wearer’s face in order to provide expected protection. This includes disposable respirators (also called “filtering facepieces”). Therefore, OSHA requires fit before a user wears a mandatory respirator on the job, and must be assessed at least annually. In addition, fit tests should be performed:
- Whenever a different size, style, model or make of respirator is used.
- When any facial changes occur that could affect fit, such as significant weight fluctuation or dental work.

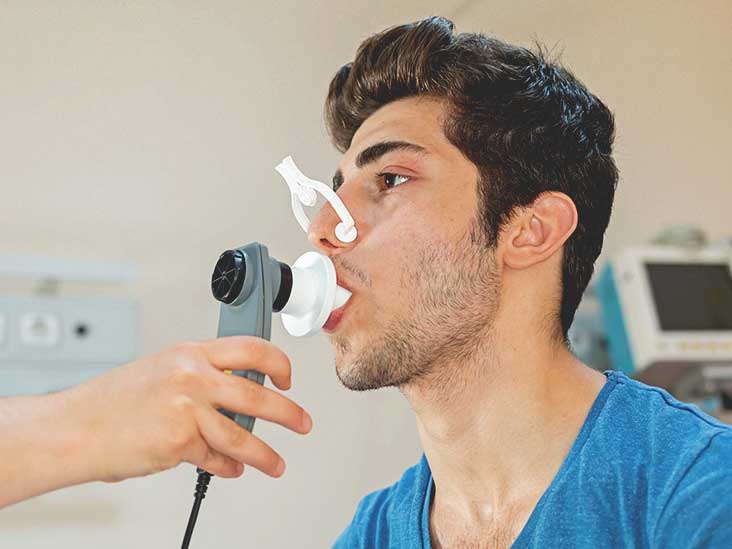
Pulmonary Fit Test
TruTest Labs are certified in performing Pulmonary Fit Test. Pulmonary function tests are a broad range of tests that measure how well the lungs take in and exhale air and how efficiently they transfer oxygen into the blood.
Understanding The TruTest Labs Pulmonary Fit Test Process
Our technical will have the individual breathe into a mouthpiece that is connected to an instrument called a spirometer. The spirometer records the amount and the rate of air that is breathed in and out over a specified time. Some of the test measurements are obtained by normal, quiet breathing, and other tests require forced inhalation or exhalation after a deep breath.
Lung volume measurement can be performed in two ways:
- The most accurate way is for a person to sit in a body plethysmograph, a sealed, transparent box that resembles a telephone booth, while breathing in and out against into a mouthpiece. Changes in pressure inside the box allow determination of the lung volume.
- Lung volume can also be measured when a person breathes nitrogen or helium gas through a tube for a specified period of time. The concentration of the gas in a chamber attached to the tube is measured, allowing estimation of the lung volume.
The diffusion capacity is measured when a person breathes carbon monoxide for a very short time, often one breath. The concentration of carbon monoxide in exhaled air is then measured. The difference in the amount of carbon monoxide inhaled and the amount exhaled allows estimation of how rapidly gas can travel from the lungs into the blood.
